Living with diabetes demands constant vigilance over blood sugar levels, which is challenging and crucial for maintaining overall health. Among the myriad strategies available, the Pinch Method for diabetes management has emerged as a novel and holistic approach. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of this method, explore what constitutes a normal blood sugar level, identify signs of high blood sugar, discuss proactive measures to lower blood sugar, and finally, uncover the mechanics of the Pinch Method for type 2 diabetes. Additionally, we will touch upon alternative treatments, offering a comprehensive view of diabetes care.
What is a Normal Blood Sugar Level?
Understanding blood sugar levels is fundamental to managing diabetes effectively. A normal blood sugar level typically falls within the range of 70 to 140 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). However, these values may vary slightly depending on factors such as age, health condition, and the timing of the blood sugar test. Consistent monitoring and maintaining blood sugar within this range are crucial for preventing complications associated with both high and low blood sugar levels.
Signs of High Blood Sugar
It is essential to recognize the signs of high blood sugar level for timely intervention and effective management. Common symptoms of high blood sugar level are – excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Prolonged periods of elevated blood sugar can result in severe complications such as cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, and kidney problems. Regular monitoring and awareness of these signs empower individuals to take necessary steps to effectively manage their condition.

What Can I Do to Lower Blood Sugar?
For individuals grappling with diabetes, adopting lifestyle modifications can transform the blood sugar level extensively. Regular exercise, enough sleep and adopting a balanced diet are cornerstones of diabetes management. Additionally, mindful eating, portion control, and monitoring carbohydrate intake contribute to better blood sugar control. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga and meditation. The collective implementation of these measures establishes a foundation for diabetes management.
How Does the Pinch Method Work for Type 2 Diabetes?
Before getting to know how this method works, what is the pinch method for diabetes? It is gaining recognition as a simple yet effective tool for managing blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes. This method involves assessing skinfold thickness, primarily in the abdominal region, to estimate the amount of subcutaneous fat. The rationale behind this approach lies in the correlation between increased abdominal fat and insulin resistance, a key factor in type 2 diabetes.
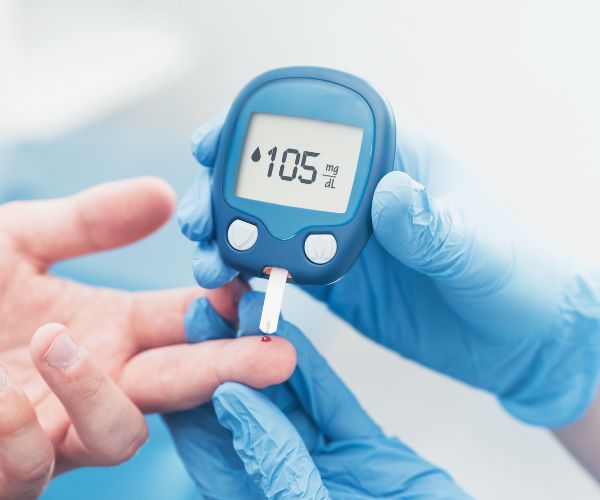
To employ the Pinch Method, one can follow these steps:
Identify the target area: The abdominal area, approximately two inches away from the navel, is the primary focus for pinch measurements.
Pinch the skin: Use the thumb and the forefinger. Now, gently pinch the skin and underlying subcutaneous fat. Avoid including muscle tissue in the pinch.
Measure skinfold thickness: Record the thickness of the skinfold in millimeters using calipers or a designated measuring tool.
Interpret the results: Regular measurements can help individuals track changes in skinfold thickness over time. A decrease in skinfold thickness may indicate improved insulin sensitivity and better blood sugar control.
It’s important to note that while the Pinch Method is valuable for managing diabetes, it should not replace conventional methods of monitoring, such as regular blood glucose testing. Consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and incorporating the Pinch Method into an overall diabetes management plan is advisable.
The simplicity and non-invasiveness of the Pinch Method make it an attractive option for the people seeking additional tools to manage their diabetes. However, it’s essential to approach this method as part of a comprehensive strategy that includes lifestyle adjustments and medical guidance. Integrating the Pinch Method into one’s routine offers a tangible, visual indicator of potential improvements in body composition and, by extension, insulin sensitivity.
Alternative Treatments to Pinch Method
While the Pinch Method presents a unique approach to diabetes management, alternative treatments, and complementary therapies also contribute to a holistic care regimen. Some noteworthy alternatives include –
Nutritional interventions:
Adopting a low-glycemic diet rich in fiber and nutrient-dense foods can positively impact blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and choosing whole, unprocessed foods can contribute to better glycemic control.
Herbal supplements:
Certain herbs, such as fenugreek and bitter melon, helps regulate the blood sugar level. However, it is advisable to get in touch with a healthcare professional before deciding to add any herbal supplements into one’s routine, as they may interact with medications or have contraindications.
Acupuncture:
This traditional Chinese medicine practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, potentially aiding in blood sugar control. While the evidence is not conclusive, some studies suggest that acupuncture may influence insulin sensitivity and improve glucose metabolism.

Mind-body practices:
Stress management techniques, including mindfulness meditation and biofeedback, improves your overall well-being and may positively influence blood sugar levels. Chronic pain/stress can exacerbate insulin resistance, making stress reduction an important component of diabetes care.
Physical activity:
Regular exercise remains a cornerstone of diabetes management. Both aerobic and resistance training exercises contribute to better blood sugar control. Tailoring exercise routines to individual preferences and capabilities ensures long-term adherence.
Conclusion
In the intricate landscape of diabetes management, the Pinch Method emerges as a novel and accessible approach for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Integrating this method into an overarching strategy that includes lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and consultation with healthcare professionals can contribute to effective blood sugar control. While the Pinch Method holds promise, it is crucial to recognize that diabetes care is multifaceted, and alternative treatments complement rather than replace conventional approaches.
By adopting a holistic mindset and individualizing care plans, individuals can navigate the challenges of diabetes with greater confidence and resilience. The synergy of conventional and alternative methods offers a comprehensive approach to address the diverse needs of individuals with diabetes. As research advances and our understanding of diabetes deepens, the evolving landscape of treatment options provides hope for improved outcomes and a higher quality of life for those living with this chronic condition.
FAQs
What is the role of insulin in lowering blood sugar?
The role of insulin in lowering blood sugar is paramount as it facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, enabling them to use it for energy. Insulin also helps store excess glucose in the liver for future energy needs, contributing to the regulation of blood sugar levels.
What is the acupressure point for diabetes?
While specific acupressure points for diabetes aren’t universally agreed upon, some practitioners focus on the point known as Spleen 6 (SP6), believed to influence blood sugar regulation. Consultation with a qualified acupressure practitioner is recommended for personalized guidance.
What are the 5 points for diabetes?
Five acupressure points often explored for diabetes include Spleen 6 (SP6), Stomach 36 (ST36), Liver 3 (LR3), Kidney 3 (KD3), and Large Intestine 4 (LI4). These points are thought to help balance energy flow and support overall well-being, but individual responses may vary.
What reduces blood sugar quickly?
Physical activity, such as brisk walking, can quickly reduce blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake by muscles. However, individual responses to exercise can vary, and consultation with a healthcare professional is advised.
Which fruits are good for diabetes?
Berries, cherries, and apples are considered good fruit choices for individuals with diabetes due to their lower glycemic index and rich fiber content. However, moderation and individualized dietary planning are crucial.
